International Energy Agency, 8 October 2015
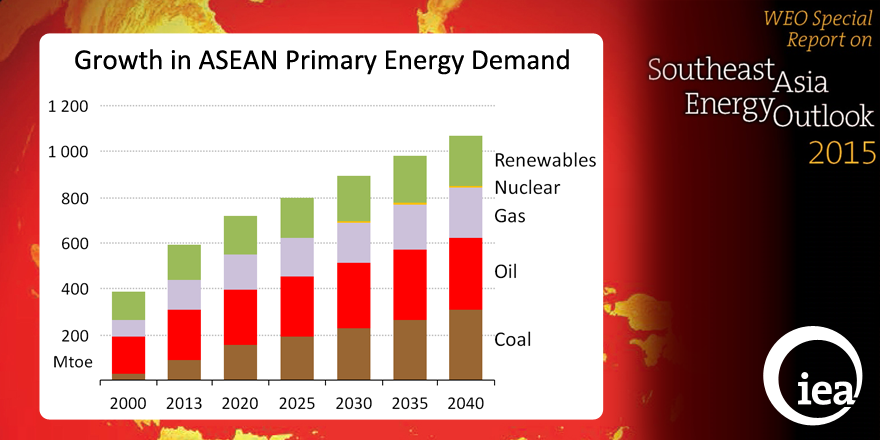
The energy landscape in Southeast Asia continues to shift as rising demand, constrained domestic production and energy security concerns lead to a greater role for coal, a sharp rise in the region’s dependence on oil imports and the reversal of its role as a major gas supplier to international markets.
“As Southeast Asia flourishes, it is moving to the centre of the global energy stage,” IEA Executive Director Fatih Birol said. “Countries in the region now have much in common with IEA members. We must all work together to build more secure and sustainable energy supplies and markets, as platforms for promoting economic development.”
The World Energy Outlook Special Report on Southeast Asia (WEO Special Report) presents a central scenario in which Southeast Asia’s energy demand increases by 80% in the period to 2040, though the region’s per-capita energy use remains well below the global average. Despite policies aimed at scaling up the deployment of renewable resources, the share of fossil fuels in the region’s energy mix increases to around 80% by 2040, in stark contrast to the declining trend seen in many parts of the world.
Rising imports sharpen the focus on the economic and security aspects of energy use. By 2040 the region’s net oil imports more than double to 6.7 mb/d, a level equivalent to the current oil imports of China. Southeast Asia’s oil import bill surges to over $300 billion per year by 2040, compared with around $120 billion in 2014, with increases in spending in almost all countries in the region.
Indonesia supports a continued expansion of Southeast Asia’s gas and coal output, but production is increasingly consumed within the region. As domestic natural gas demand outpaces indigenous production, intra-regional and intra-country trade increases, and Southeast Asia turns into a net gas importer of around 10 bcm by 2040, compared with net exports of 54 bcm in 2013.
The power sector shapes the energy outlook for Southeast Asia, as electricity demand almost triples by 2040, an increase greater than the current power output of Japan. The sector continues its shift towards coal due to its abundance and relative affordability. Although the average efficiency of Southeast Asia’s coal-fired power plant fleet increases by 5 percentage points throughout the projection period, less-efficient subcritical technologies account for 50% of the region’s coal power fleet in 2040, highlighting the need to accelerate the deployment of more efficient technologies in the region to reduce local pollution and slow the rise in CO2 emissions.
The energy landscape in Southeast Asia continues to shift as rising demand, constrained domestic production and energy security concerns lead to a greater role for coal, a sharp rise in the region’s dependence on oil imports and the reversal of its role as a major gas supplier to international markets.

“As Southeast Asia flourishes, it is moving to the centre of the global energy stage,” IEA Executive Director Fatih Birol said. “Countries in the region now have much in common with IEA members. We must all work together to build more secure and sustainable energy supplies and markets, as platforms for promoting economic development.”
The World Energy Outlook Special Report on Southeast Asia (WEO Special Report) presents a central scenario in which Southeast Asia’s energy demand increases by 80% in the period to 2040, though the region’s per-capita energy use remains well below the global average. Despite policies aimed at scaling up the deployment of renewable resources, the share of fossil fuels in the region’s energy mix increases to around 80% by 2040, in stark contrast to the declining trend seen in many parts of the world.
Rising imports sharpen the focus on the economic and security aspects of energy use. By 2040 the region’s net oil imports more than double to 6.7 mb/d, a level equivalent to the current oil imports of China. Southeast Asia’s oil import bill surges to over $300 billion per year by 2040, compared with around $120 billion in 2014, with increases in spending in almost all countries in the region.
Indonesia supports a continued expansion of Southeast Asia’s gas and coal output, but production is increasingly consumed within the region. As domestic natural gas demand outpaces indigenous production, intra-regional and intra-country trade increases, and Southeast Asia turns into a net gas importer of around 10 bcm by 2040, compared with net exports of 54 bcm in 2013.
The power sector shapes the energy outlook for Southeast Asia, as electricity demand almost triples by 2040, an increase greater than the current power output of Japan. The sector continues its shift towards coal due to its abundance and relative affordability. Although the average efficiency of Southeast Asia’s coal-fired power plant fleet increases by 5 percentage points throughout the projection period, less-efficient subcritical technologies account for 50% of the region’s coal power fleet in 2040, highlighting the need to accelerate the deployment of more efficient technologies in the region to reduce local pollution and slow the rise in CO2 emissions.
No comments:
Post a Comment
Climate Science welcomes your views/messages.